Ionic Propulsion in Atmosphere (IPROP)
- contact:
- funding:
The European Innovation Council (Grant agreement ID: 101098900)
- Partner:
Politecnico di Milano
Università di Bologna
Von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics
Institut Superieur de l’Aeronautique et de l’Espace
Centre National de la Recherce Scientifique
Aeronord di Enzo Cisaro & C. s.a.s.
Technische Universität Dresden
Project description
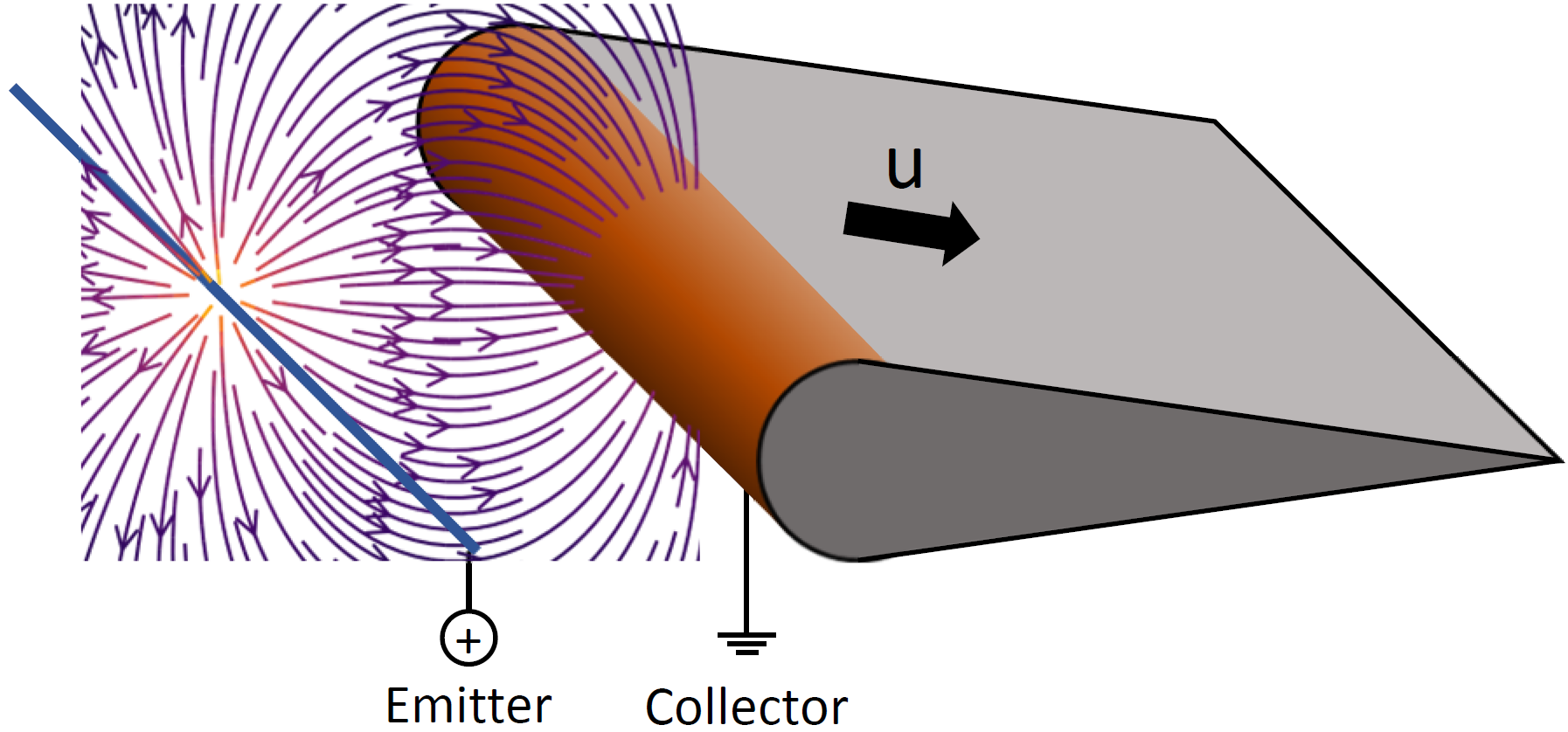
Ionic propulsion in space applications has already reached maturity. On the other hand, ionic propulsion in atmosphere has yet to achieve meaningful applications. The IPROP Project aims to change the status quo and launch a demonstrator airship powered by this technology, marking the first step towards pseudo-satellite applications. Due to the lack of moving parts and good efficiency, ionic propulsion could prove to be well suited for this application and offer a more flexible, cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution to satellites for a broad range of missions.
To achieve these goals, ionic propulsion is to be evaluated more rigorously on the grounds of combined theoretical, numerical and experimental research efforts within IPROP.
For more details and the state of research of the project, visit https://www.iprop-project.eu/.
Work at ISTM
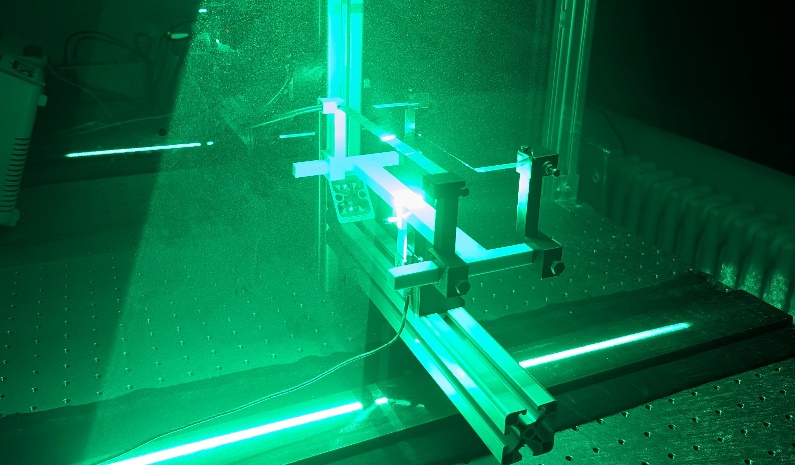
Building on prior knowledge with dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) actuators, research effort at ISTM revolves around the development of a precise and robust performance evaluation metric to comprehensively examine various electro-aerodynamic thruster devices for stratospheric airships. Multiple measurement techniques are evaluated and compared, ranging from force measurements to a variety of (laser-)optical flow diagnostics. Currently, experiments are conducted in quiescent air, with plans for expanding to moving air, atmospheric pressure conditions, larger wingspans and multiple actuator array configurations as well as long-term material studies.